What is Menopause?
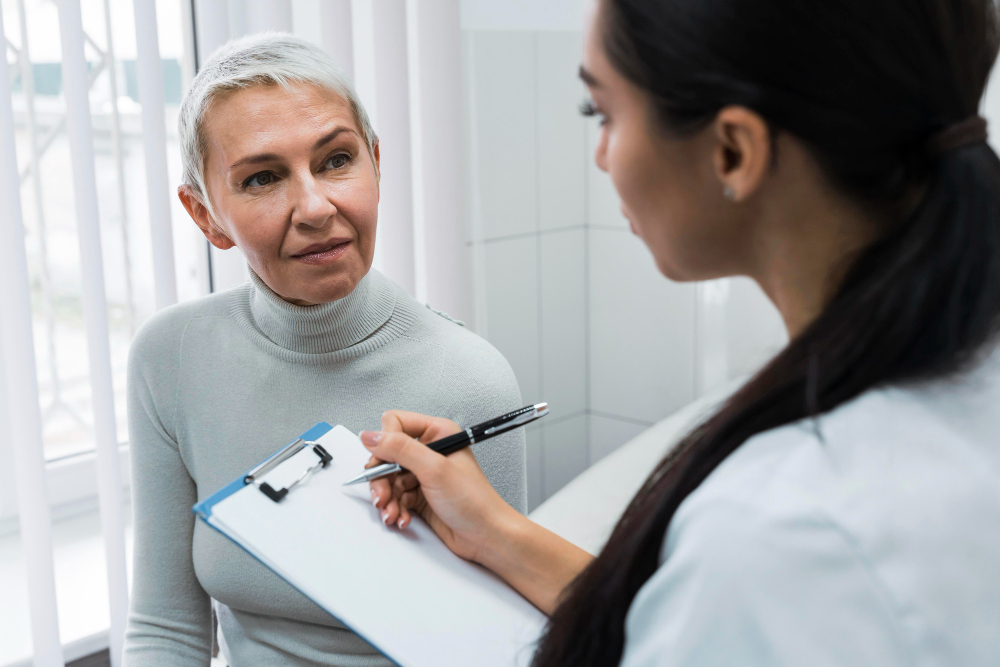
Menopause is a natural stage in a woman’s life. It marks the end of monthly periods and fertility. Usually, menopause happens between ages 45 and 55. However, it can occur earlier or later for some women. During menopause, the body makes less estrogen and progesterone. These are important female hormones. Because of these changes, women may notice new symptoms. Menopause is a normal part of aging, but it can affect daily life. Understanding menopause helps women prepare and manage symptoms better.
Common Symptoms of Menopause
Many women experience different symptoms during menopause. Some symptoms are mild, while others can be more bothersome. For example, hot flashes are a common sign. These are sudden feelings of heat in the body. Night sweats, which are hot flashes during sleep, can also occur. In addition, women may notice changes in mood or sleep patterns. Here are some common menopause symptoms:
Because symptoms can vary, not every woman will have all of these. Still, knowing what to expect can help you feel more in control.
How is Menopause Diagnosed?
Doctors usually diagnose menopause based on symptoms and age. For most women, no special tests are needed. However, sometimes a doctor may suggest blood tests. These tests check hormone levels, such as estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). If periods have stopped for 12 months in a row, menopause is likely. In some cases, doctors may rule out other causes for symptoms. For example, thyroid problems can mimic menopause. Always talk to your doctor if you are unsure about your symptoms.
Treatment Options for Menopause
There are many menopause treatment options available. The right choice depends on your symptoms and health history. Some women do not need any treatment. Others may need help managing symptoms. Here are some common treatments:
Because every woman is different, treatment should be tailored to your needs. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and World Health Organization (WHO) recommend discussing risks and benefits with your doctor.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Menopause
Healthy habits can make menopause easier to manage. For instance, regular exercise helps control weight and boosts mood. Eating a balanced diet supports bone and heart health. Here are some simple tips:
Because small changes can make a big difference, try adding one new habit at a time.
Prevention and When to Seek Help
Although menopause cannot be prevented, you can prepare for it. Early planning helps you handle symptoms better. For example, regular check-ups can catch health issues early. You should see a doctor if:
Because some symptoms may signal other health problems, it is important to get checked. Early care leads to better outcomes.
In summary, menopause is a normal part of life. However, symptoms can be managed with the right support. Consult a healthcare specialist for personalized menopause guidance.